Bitcoin revolutionized how the world pays, giving you the power to control your money without governments or banks. However, its transaction processing limits have long been said to be a shortcoming. The Bitcoin Lightning Network helps this issue by giving users the ability to make hundreds of thousands of cheap transactions each second. Here is the Lightning Network explained.
Lighting Network Explained
The Lightning Network is a secondary layer on the Bitcoin blockchain which allows users to create payment channels where transactions can occur away from the main blockchain, but still benefit from the blockchain’s security and decentralization. These are known as off-chain transactions. The second layer offers speed, cost savings and scalability for the entire Bitcoin network.
How Does the Lightning Network Work?
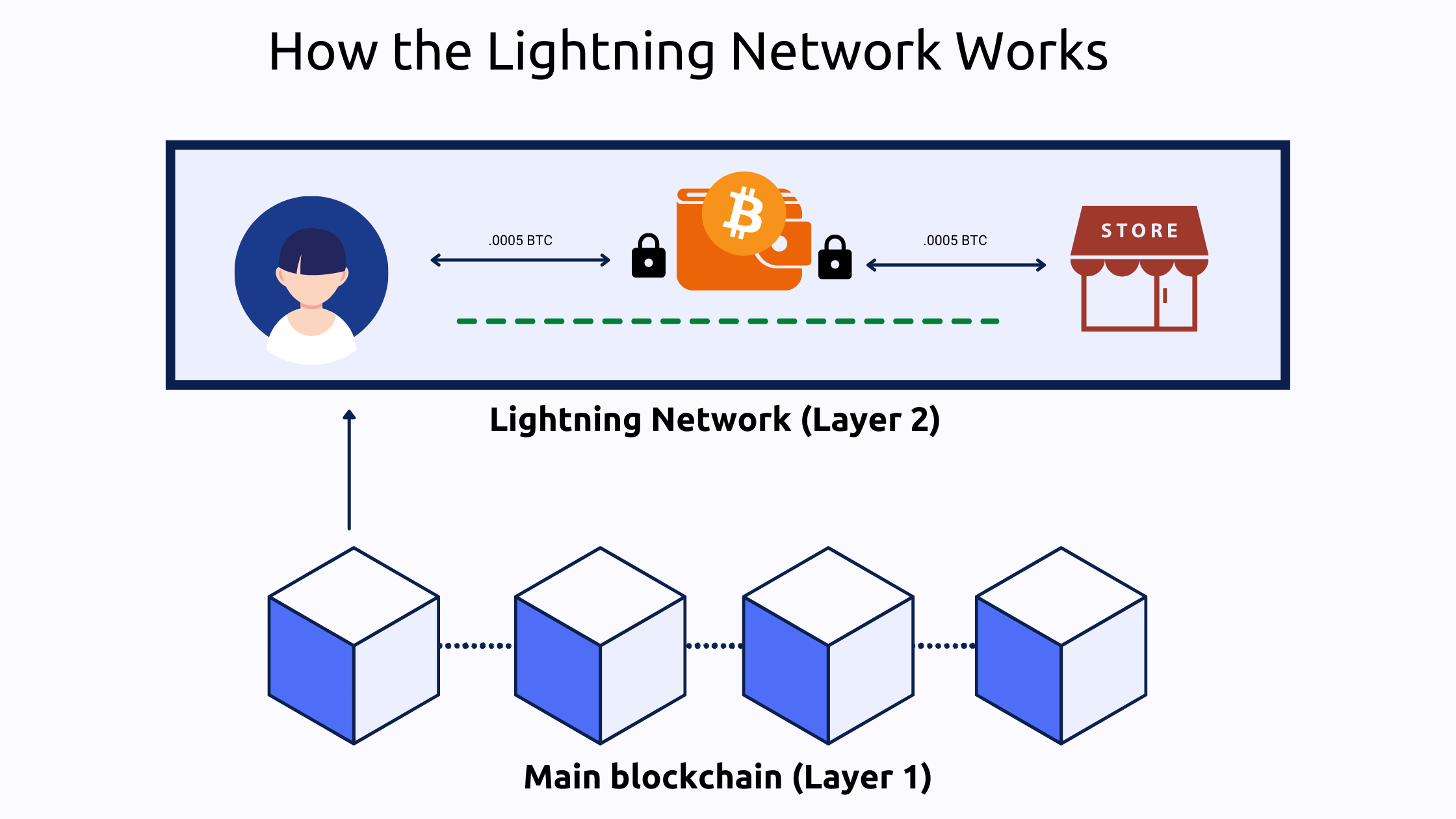
The Lightning Network is built upon smart contracts that create off-chain payment channels between two parties. These are direct payment lines that occur on top or outside of the main blockchain. For example, you and your local cafe can create a payment channel in which you pay for your daily coffee and scone. Once the payment channel is open, you can make an unlimited number of payments. Transactions occur instantly and at a fraction of what it would cost on the main blockchain. Your payment channel has its own ledger where the transactions are recorded away from the main Bitcoin blockchain. Each party has the power to close or renew at their discretion.
Once the two parties decide to close the payment channel, all of the transactions that occurred inside are consolidated and then broadcasted to the main blockchain ledger. Consolidating the smaller transactions allow for larger transactions to be validated in a quick manner. Without payment channels, your small coffee and scone transactions would get in the way of the larger transactions, slowing down the Bitcoin network for everyone.
You could, of course, buy your coffee and scone through a normal Bitcoin transaction. However, each time you order you would have to pay the network fees which may cost more than the coffee itself. What’s the use in that? Instead with the Lightning Network, the only fees you pay are to open and close the payment channel.
What Makes the Lightning Network So Great?
The combination of payments made through the main Bitcoin blockchain and through Lightning Network result in an overall better payment experience that is fast, low cost and scalable.
It’s Fast
Exactly how fast is the Lightning Network? The Lightning Network is capable of handling 1,000,000 transactions per second, while the main Bitcoin blockchain can handle around 7 transactions per second.
It’s Cheap
Fees for Bitcoin transactions can be expensive (sometimes greater than whatever you're paying for). Lightning Network provides an economical way to make payments of any size, at regular intervals. This opens the door for making everyday micropayments in Bitcoin, like for coffee, pizza or anything else you can buy with Bitcoin.
It’s Scalable
The Lightning Network allows users to jump through payment channels. If Party A is connected to Party B, and Party B is connected to Party C, then Party A can transact with Party C without opening a new payment channel.
Technical Innovations and Features
One of the key technologies behind the Lightning Network is Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs).
HTLCs help the Lightning Network send secure and trustless transactions off-chain. They also Enable multi-hop payments, where funds are routed through multiple nodes.
HTLCs are a type of smart contract. Their function is to enable conditional payments. They do this by combining two cryptographic techniques: hashlocks and timelocks.
The hashlock mechanism works by having the sender create a transaction that includes a cryptographic hash. The recipient can only claim the funds if they provide the correct corresponding hash.
The timelock mechanism means that the transaction has a time limit attached to it. If the recipient doesn’t claim the funds in time, the sender can take them back.
There have also been quite a few tech updates to the Lightning Network in recent years.
Taproot
Activated in 2021, Taproot was a significant upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol. It allows for more complex transactions without revealing all the details on the blockchain, increasing privacy. Taproot also reduces the size of complex transactions, which results in lower transaction fees and greater scalability. These changes apply to the Lightning Network as well as the base layer of Bitcoin.
Wumbo Channels
To reduce risk, the Lightning Network previously had a limit on channel sizes. The introduction of Wumbo Channels raised this limit. Thanks to this innovation, the network’s liquidity has been enhanced due to the ability to transfer larger payments.
Multipath Payments
Multipath payments, also known as multi-hop payments, involve splitting a single payment into multiple smaller payments that are then routed through different paths along the network. This both reduces the likelihood of transaction failures and optimizes the use of available liquidity on the network.
These are only a few of the most significant upgrades that Lightning has seen. As the layer-2 network continues to grow and evolve, developers will continue to introduce more updates.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the Lightning Network’s growing adoption and innovation, some notable challenges remain. For example, smaller nodes might not have the capacity or capital necessary to move user’s funds. The user experience has sometimes been plagued by bugs in the interface. Even without bugs, anyone who has attempted to set up a Lightning wallet knows that the process is more complex than that of a standard Bitcoin wallet.
Even in the face of these obstacles, Lightning marches on. On April 3rd, 2024, Coinbase announced it would be rolling out Lightning on its platform. In March 2024, Lightning company Neutronpay secured $1.5 million in venture capital funding to improve the network’s infrastructure in Southeast Asia.
Lightning Network vs On-chain Payments and Other L2 networks
As mentioned, Lightning transactions are faster and cheaper than on-chain transactions. However, there’s also a higher chance of failure due to lack of liquidity, and sometimes the party you want to send a Lightning payment to doesn’t have a channel open. For these reasons, Lightning has its share of competitors, both on Bitcoin and other blockchains.
Polygon, for example, is a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum network. It functions in a manner similar to Lightning. Developers find Polygon attractive due to its ability to enable decentralized applications (dApps) to function more smoothly. There may be even more demand for Polygon than Lightning due to the fact that BTC tends to be seen as more of a store of value, while Ethereum’s ETH token powers a litany of dApps.
Raiden is another layer-2 that sits atop Ethereum. In addition to transaction details, Raiden’s state channels also transfer smart contract details.
History of Lightning Network
- 2013: Bitcoin developer Mike Hearn publishes Satoshi Nakamoto’s explanation of payment channels.
- 2015: Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja publish their paper “The Bitcoin Lightning Network” in which they describe an off-chain payment protocol built with payment channels.
- 2016: Lightning Labs is founded. The company is dedicated to advancing the Lightning Network.
- 2018: Lightning Labs releases beta Lightning implementation. Lightning Labs receives $2.5 million in seed funding, with notable investors including Square founder Jack Dorsey.
- 2022: BitPay supports Lightning Network payments
Lightning’s rising usage
While the Lightning Network is still in its infancy, the channel continues to make headway in pushing fast, scalable crypto payments forward.
Across the BitPay platform, Lightning Network payments make up about 3% of total payments, showing especially high payments across the VPN/Hosting and Video Game sectors.
As a low cost, fast payment option, Lightning Network payments typically tend to be lower in transaction value compared to Bitcoin and other traditional network payments. As of April 2024, the average Lightning payment was $130, compared to Bitcoin payments averaging upwards of $1,000.
Not all crypto wallets support sending and receiving Lightning payments. However, of those that do, the top wallets used for Lightning payments are:
- Square Cash
- Wallet of Satohshi
- Phoenix
- Muun
- Exodus
- Electrum
For more Lightning Network usage data, head over to BitPay’s Stats center.
How to Use the Lightning Network in BitPay
Ready to jump into the Lightning Network? BitPay makes it easy to send and receive Lightning payments.
How to Make Lightning Payments
Making a Lighting payment to a BitPay merchant is as easy as any other payment. Once an invoice is generated, you will have the opportunity to select your Lightning supported wallet. You can find a list of Lightning wallets BitPay supports in our Support section.
How to Accept Lightning Payments
Your customers will automatically have the ability to choose a Lightning Network payment. As a BitPay merchant, you will not have to make any changes or adjustments to start accepting Lightning payments.
Looking Forward to the Next Era of Lightning Payments
Lightning is an important advancement not only for Bitcoin, but also for the blockchain and crypto sector as a whole. Discovering what is possible with layer-2’s, and what problems they tend to encounter, has tremendous implications for all related technologies.
And of course, addressing the scalability issues that Bitcoin faces can be seen as one of the most important things for its future. Bitcoin is both the most secure and most decentralized blockchain, but it is also the least scalable. Lightning has the potential to be the ultimate solution, currently presenting a promising step forward in BTC payments.
FAQs About the Bitcoin Lightning Network
How fast is the Bitcoin Lightning Network? How Many transactions per seconds can the Bitcoin Lightning Network process?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is capable of processing 1,000,000 transactions per second (TPS). By comparison, Bitcoin can process about 7 TPS, while Visa can process tens of thousands TPS.
How Do I Use the Lightning Network?
When paying a BitPay merchant, you will have the option to pay invoices via Lightning Network. Simply scan the invoice QR code, choose your wallet and select Lightning Network as your cryptocurrency. A Lightning enabled wallet is required to use the Lightning Network.
Which coins are supported by the Lightning Network?
BitPay’s support of Lightning Network only extends to Bitcoin transactions.


